The Relationship Between Igneous Rocks & Tectonic Plates
The relationship between igneous rocks and tectonic plates is fundamental to understanding Earth's geology. Igneous rocks form from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava, and their formation is deeply tied to the movement and interactions of tectonic plates. These interactions occur at divergent, convergent, and transform boundaries, each creating unique conditions for igneous rock formation.
Igneous Rocks
Let's say you're on a scavenger hunt and the last item you need to find is an igneous rock. You learned that igneous rocks are rocks that form from the cooling and solidifying of magma or lava, which is the name given to magma that reaches the surface of the earth and the stuff you think of flowing down the side of a volcano.
Armed with this knowledge you might hop on a plane and fly to the closest active volcanic mountain to hunt for an igneous rock.
General Classification of Igneous RocksWell, this would be one option open to you, but did you know that igneous rocks can also be found at the bottom of the ocean as well as deep underground? This is because igneous rock formation is linked to the movement of tectonic plates. we will learn more about tectonic plates and how their movements lead to the formation of igneous rocks.
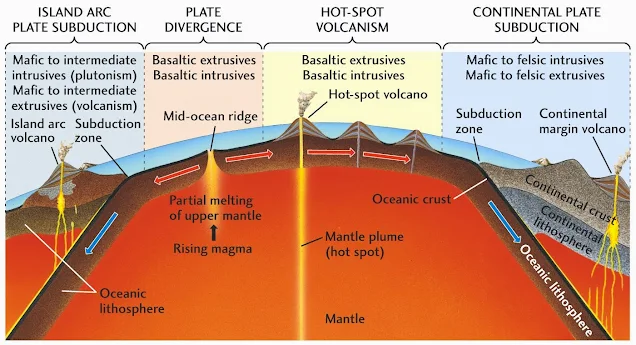
Tectonic Plates
So let's start by making sure we understand what tectonic plates are. There is a theory, called plate tectonics, which states that the Earth's crust is broken up into plates. In other words, if you were to strip everything off of the Earth's surface and drain all of the water, the remaining shell of the planet would look like it was cracked, much like the fractures that happen when you crack the shell of a hardboiled egg.
The plate-like sections of earth's crust are called tectonic plates.
These massive tectonic plates are able to move and they basically float on top of the hot, deep layers of the earth. These hot, deep layers are where we see magma forming. As these plates float around, they interact with each other. They can either get closer together or drift apart, and this tectonic plate movement gives us the right conditions for the formation of igneous rocks.
What's the difference between an active and passive continental margin?Diverging Tectonic Plates
When tectonic plates move apart, or diverge, they create opportunities for the Earth's internal dynamics to surface. This process is pivotal in the formation of igneous rocks. As these colossal plates of the Earth's crust slowly separate, magma from beneath the crust rises through the newly formed gaps to reach the surface.
Divergent boundaries, where tectonic plates move away from each other, are key sites for igneous rock creation. A prime example of this phenomenon is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a submarine mountain range stretching across the Atlantic Ocean. Here, the magma that emerges cools against the ocean's cold waters, solidifying into igneous rock.
The Connection Between Divergent Boundaries and Igneous Rocks:
Magma Generation: At these boundaries, the mantle material rises due to the reduction in pressure, causing it to melt through a process known as decompression melting. This generates magma.
Cooling and Solidification: Once the magma reaches or nears the surface, it begins to cool. The cooling rate and the magma's composition determine the type of igneous rock that forms:
- Extrusive Igneous Rocks: When magma erupts onto the surface as lava, it cools rapidly. This quick cooling results in fine-grained rocks like basalt, commonly seen on ocean floors and in volcanic areas.
- Intrusive Igneous Rocks: If magma cools slowly beneath the surface, it forms coarse-grained rocks such as gabbro, often found in the roots of ancient mountain ranges or deep within the Earth's crust.
This interplay between tectonic movements and magma behavior not only shapes the Earth's surface but also contributes significantly to our understanding of geological processes.
Converging Tectonic Plates
When tectonic plates converge, or move toward each other, they engage in a dance of geological forces that significantly influences the formation of igneous rocks. Here's how this convergence shapes the Earth's crust:
Understanding Convergent Boundaries and Igneous Rock Formation:
Types of Convergent Boundaries
Oceanic-Oceanic Convergence: When two oceanic plates collide, one is forced beneath the other in a process called subduction. As the subducting plate descends into the mantle, it heats up, releasing water and other volatiles into the overlying mantle. This hydration leads to partial melting of the mantle, generating magma.
Oceanic-Continental Convergence: Here, an oceanic plate subducts beneath a continental plate. Similar to oceanic-oceanic convergence, the subducting plate melts due to the increased heat and pressure, creating magma that rises through the crust.
Continental-Continental Convergence: Although less common, when two continental plates collide, they can form massive mountain ranges. Here, igneous activity is less about new magma generation and more about the reworking of existing rock through metamorphism, though some magmatic processes can still occur.
Formation of Igneous Rocks at Convergent Boundaries:
Magma Generation: The subduction process at oceanic-oceanic or oceanic-continental boundaries causes the mantle to melt, producing magma. This magma can be quite varied in composition, leading to different types of igneous rocks.
Volcanic Activity: The magma often ascends to the surface, leading to volcanic eruptions. These eruptions can create:
- Extrusive Igneous Rocks: Lava from these volcanoes cools quickly upon reaching the surface, forming fine-grained rocks like andesite or basalt. The Pacific Ring of Fire, known for its high volcanic activity, is a prime example where such rocks are prevalent.
- Intrusive Igneous Rocks: Not all magma reaches the surface; some cools and solidifies within the Earth's crust, creating coarse-grained rocks like granite or diorite. These are often found in regions associated with ancient or ongoing subduction zones, such as the Sierra Nevada batholith in California.
Plutons and Batholiths: Over time, multiple intrusions of magma can accumulate and form large bodies of rock known as plutons or, if vast enough, batholiths. These structures are significant in understanding the geological history and tectonic activity of an area.








