Chlorastrolite: Michigan's State Gemstone
Chlorastrolite is a gemstone variety of the mineral pumpellyite, known for its unique, radiating star-like patterns. It's characterized by its green color, often with darker green or black inclusions, creating a mottled or star-like appearance. It's primarily found in Michigan's Upper Peninsula.
Chlorastrolite, also known as Isle Royale Greenstone, is a green or bluish green stone found in the Keweenaw Peninsula of Upper Michigan and Isle Royale in Lake Superior. It is the official state gemstone of Michigan. It's a green gemstone with a distinctive chatoyancy (cat's eye effect) that can resemble a turtle shell pattern.
Chlorastrolite is prized for its distinctive, radiating, star-like patterns. These patterns are due to the fibrous or acicular (needle-like) crystals that grow in a radial pattern. The color can range from green to black, often with a chatoyant effect, meaning it displays a shifting, luminous band of color when viewed from different angles.
 |
| Chlorastrolite Specimens. Photo: Wild Superior Gems |
The name chlorastrolite comes from three Greek words: "chloros" meaning green, "astron" meaning star, and "lithos" meaning stone. This refers to the stone's color and its stellate (star-shaped) structure, which scatters light and creates a chatoyant or shimmering effect. Chlorastrolite is a variety of the mineral pumpellyite and forms in the cavities of basaltic lava flows.
Isle Royale has long been famous as the home of chlorastrolite, known informally in rock-collecting and lapidary circles as "Isle Royale greenstone." Cholorastrolite is a variety of pumpellyite: Ca2(Mg,Fe)Al2(SiO4)(Si2O7)(OH)2·H2O.
Chlorastrolite was first discovered in 1847 on Isle Royale by C.T. Jackson and J.D. Whitney. In 1972 the governor of Michigan signed a bill designating chlorastrolite as the official state gem.
Many people wonder why Chlorastrolite is the state gem when Petoskey Stone seems more common. The answer is simple: Michigan has two special rocks: Petoskey Stone, the official state stone, and Chlorastrolite, the official state gemstone. While Petoskey Stone is more well-known, Chlorastrolite officially holds the gem title.
Chlorastrolite Formation
Chlorastrolite's formation is a fascinating geological story involving ancient volcanic activity and metamorphic processes. Here's a breakdown:
Volcanic Activity: Around 1.1 billion years ago, volcanic eruptions spewed lava rich in copper and calcium. This lava cooled and solidified into rocks called basalts.
Metamorphism: Over millions of years, these basalts were subjected to intense heat and pressure deep within the Earth's crust. This process, called metamorphism, transformed the basalts into new rock types, including a rock called chlorastrolite schist.
Hydrothermal Alteration: As hot, mineral-rich fluids circulated through the chlorastrolite schist, they interacted with the rock, replacing some minerals with others. This process introduced elements like chromium and iron, responsible for Chlorastrolite's distinctive green color.
Chatoyancy: The fibrous nature of Chlorastrolite, combined with the presence of microscopic mineral inclusions, creates the gemstone's signature chatoyancy or cat's eye effect. Light interacts with these inclusions, reflecting a shimmering band of light across the stone's surface.
Where is Chlorastrolite found
Chlorastrolite is primarily found
in the United States around Lake Superior particularly near beaches
like Agate Beach and Black Rocks. More specifically, it can be found in
the Keweenaw Peninsula of Michigan's Upper Peninsula and on Isle Royale .
Isle Royale is a National Park, and it is illegal to collect
Chlorastrolite specimens there. However, Chlorastrolite can sometimes be
found in loose sediments or as beach pebbles after being eroded from
the basalt by water and wave action. However, collecting gemstones from
public lands in Michigan has regulations, so be sure to check permit
requirements before heading out.
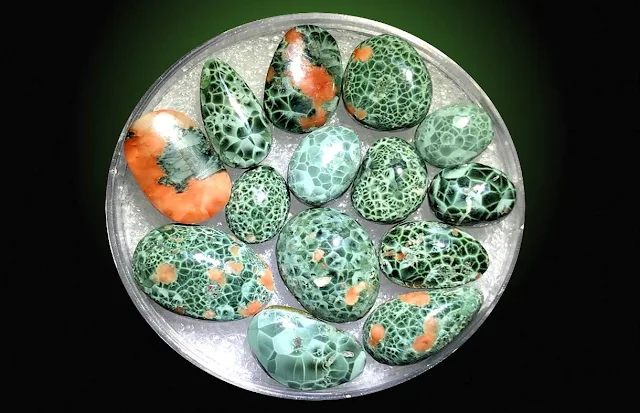
Appearance of Chlorastrolite
Chlorastrolite often forms in grape-like clusters or kidney-shaped masses, creating a bumpy, textured surface. When cut and polished, some Chlorastrolite specimens reveal a radiating starburst pattern due to the arrangement of its fibers. The most striking feature of Chlorastrolite is its vibrant green color. This can range from a deep, forest green to lighter, more olive or bluish hues. Chlorastrolite typically has a glassy, shiny luster, reflecting light like a polished surface. This luster can be enhanced by polishing and cutting.
 |
| Chlorastrolite: Michigan's Striking State Gemstone. Chlorastrolite from Isle Royale National Park, Lake Superior, Keweenaw Co., Michigan Photo: Adam Johnson |
Properties of Chlorastrolite
Composition: Chlorastrolite is not a single mineral, but rather a member of the pumpellyite mineral group. Its chemical composition can vary depending on its specific location and type. However, The chemical formula of Chlorastrolite is Ca2(Mg,Fe)Al2(SiO4)(Si2O7)(OH)2·H2O.
Physical Properties
- Color: Chlorastrolite is primarily known for its distinctive green color, ranging from light olive green to deep bluish-green and even greenish-black. Some specimens can exhibit brown, white, blue, or pinkish-brown areas.
- Luster: Chlorastrolite typically exhibits a vitreous (glassy) luster, although it can also appear dull or silky when fibrous.
- Crystal System: Chlorastrolite crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system.
- Streak: The streak of chlorastrolite is usually white, but it can be light green or grey depending on the composition.
- Hardness: Chlorastrolite has a Mohs hardness of 5 to 5.5, meaning it can be scratched by steel and harder minerals.
- Cleavage: Chlorastrolite typically does not have distinct cleavage, but it can fracture conchoidally, resulting in smooth, curved fracture surfaces.
- Crystal Form: Chlorastrolite often occurs as fibrous or radiating aggregates, but it can also form prismatic crystals with a radial starburst pattern when cut and polished.
- Density: The specific gravity of chlorastrolite varies from 2.7 to 3.0, depending on its composition.
- Transparency: Chlorastrolite can be translucent to opaque, with the degree of transparency depending on its density and the presence of inclusions.
- Fracture: Chlorastrolite tends to fracture conchoidally, meaning it breaks into smooth, curved pieces.
- Specific Gravity: As mentioned above, the specific gravity of chlorastrolite varies from 2.7 to 3.0.
- Solubility: Chlorastrolite is insoluble in water and most common acids.
- Magnetism: Chlorastrolite is not magnetic.
Optical Properties
- Fluorescence: Chlorastrolite can exhibit weak fluorescence under longwave UV light, with colors ranging from green to yellow-green.
- Pleochroism: Chlorastrolite can exhibit weak pleochroism, meaning its color can vary slightly depending on the viewing direction.
- Refractive Index: The refractive index of chlorastrolite varies between 1.674 and 1.722, depending on its specific composition.
Additional Properties
Inclusions: Chlorastrolite can often contain inclusions of other minerals, such as quartz, calcite, pyrite, or manganese oxides. These inclusions can add unique patterns or textures to the gemstone.
 |
| Greenstone (Chlorastrolite) Photo: Jeff Kopsi |
What is special about Chlorastrolite?
Rarity: Gem-quality chlorastrolite is quite rare, and most stones are very small. The largest deposits of chlorastrolite are found on Isle Royale in Lake Superior, which is a National Park and off-limits to collecting.
Unique beauty: It has a green or bluish green color with a "turtleback" pattern caused by finely radiating or stellate masses that exhibit chatoyancy, or a varying luster. This chatoyancy can be subtranslucent to opaque, giving the stone a depth and mystery.
Historical significance: Chlorastrolite has been used in jewelry and decorative objects for centuries, especially by Native American tribes in the Great Lakes region.
State gemstone: Chlorastrolite is the official state gemstone of Michigan.
 |
| Greenstone (Chlorastrolite) Photo: Wild Superior Gems. |
Overall, Chlorastrolite is a visually captivating gemstone with a unique combination of color, luster, texture, and pattern. Its organic forms, chatoyant brilliance, and fascinating inclusions make it a truly special and mesmerizing treasure.
 |
| Greenstone (Chlorastrolite) Photo:Wild Superior Gems |
See also:
Benitoite: The Rarest Gemstone Found Only in California
Top Spots For Gem Hunting In The US II
Larimar: The Blue Stones of Atlantis


.jpg)