Reticulite: Vesicular Volcanic Rock
Reticulite is a volcanic rock characterized by a high content by volume of bubbles of volcanic gas that gives as a crosslinked foam.
Reticulite is a type of pumice that is extremely vesicular, meaning it has a lot of tiny holes or bubbles. It is formed when basaltic lava, which is a type of lava that is low in silica, is erupted from a volcano. The lava is shot into the air at high velocity, and as it cools, the gas bubbles within it expand and form the tiny holes that characterize reticulite.
Reticulite is a valuable tool for geologists, as it can be used to determine the age of volcanic rocks. The size and shape of the bubbles in reticulite can be used to estimate the temperature and pressure at which the rock was formed. Reticulite can also be used to identify the source of volcanic rocks, as different volcanoes produce reticulite with different characteristics.
Reticulitis is formed when the lava is abruptly cooled, solidifying so rapidly that it does not allow the release of the gases contained in the bubbles after being ejected by a powerful lava source. The resulting material is a very fragile volcanic glass, in which the numerous rapidly expanding bubbles in the still-fluid lava interlock and fuse, creating the characteristic lattice structure of this rock.
 |
| Reticulite from Kīlauea volcano, Hawaii. Left Image credit: James St. John, right image credit: Causeway Minerals |
Although it is sometimes considered a form of basaltic pumice stone , unlike true pumice stone, and despite its lightness, reticulite does not float on the surface of the water due to its open bubble structure with walls much thicker than walls Of the microscopic or sub-microscopic bubbles that predominate in pumice. With a porosity that can reach 98%, reticulitis is the least dense rock known on Earth.
It is so delicate it can be crushed between one's fingers, and it can't be expected to last long in most geological environments.
 |
| A delicate framework of golden reticulite, also known as thread lace scoria. Credit: Causeway Minerals |
Reticulite Properties
Texture
- Extremely vesicular: The defining characteristic of reticulite is its honeycomb-like network of interconnected glass strands. This high void space results in a very light and porous texture.
- Fragile: Due to the delicate nature of the glass threads, reticulite is easily broken and requires careful handling.
Origin:
- Basaltic: Reticulite forms from rapidly cooling basaltic lava fountains, typically exceeding 300 meters in height. The violent eruption causes gas bubbles to expand and create the characteristic network during solidification.
- Indicator of high-energy eruptions: The presence of reticulite suggests a forceful and explosive volcanic event.
Chemical Composition:
- Amorphous silicate glass: While the exact composition can vary slightly depending on the specific lava source, reticulite is primarily composed of amorphous silicate glass, similar to other volcanic glasses.
- Trace elements: Depending on the specific origin, reticulite may contain trace elements like iron, titanium, and magnesium.
Color:
- Golden-brown: The glass network typically exhibits a warm, golden-brown hue, though lighter and darker shades can occur.
- Influenced by sunlight: Reticulite can appear slightly darker when wet and may lighten in direct sunlight.
Mineral Composition:
- Non-crystalline: Unlike most rocks, reticulite lacks a defined crystal structure and is classified as a non-crystalline rock.
- May contain volcanic glass minerals: Occasionally, small mineral crystals of volcanic glass like tridymite or cristobalite might be present within the network.
 |
| Reticulite: Vesicular Volcanic Rock. Credit: Causeway Minerals |
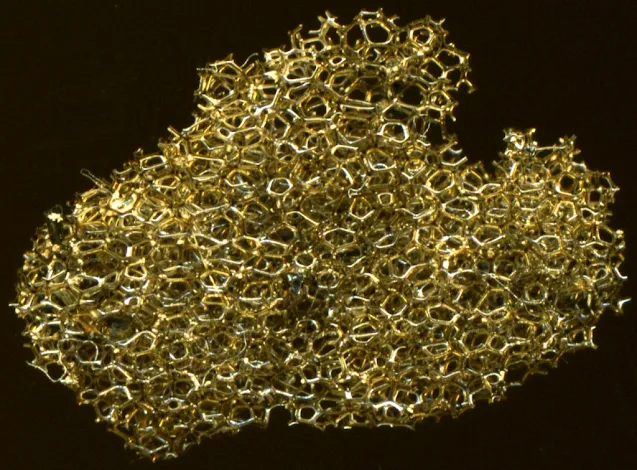 |
| Reticulite from Kīlauea volcano, Hawaii. Credit: Causeway Minerals |
 |
| Reticulite Pumice. Credit: Causeway Minerals |

%20(1).webp)






